Workspaces
This application is used to edit the Workspace item.
Workspaces are an important notion in Aquarium. Find more information about them in the dedicated section.
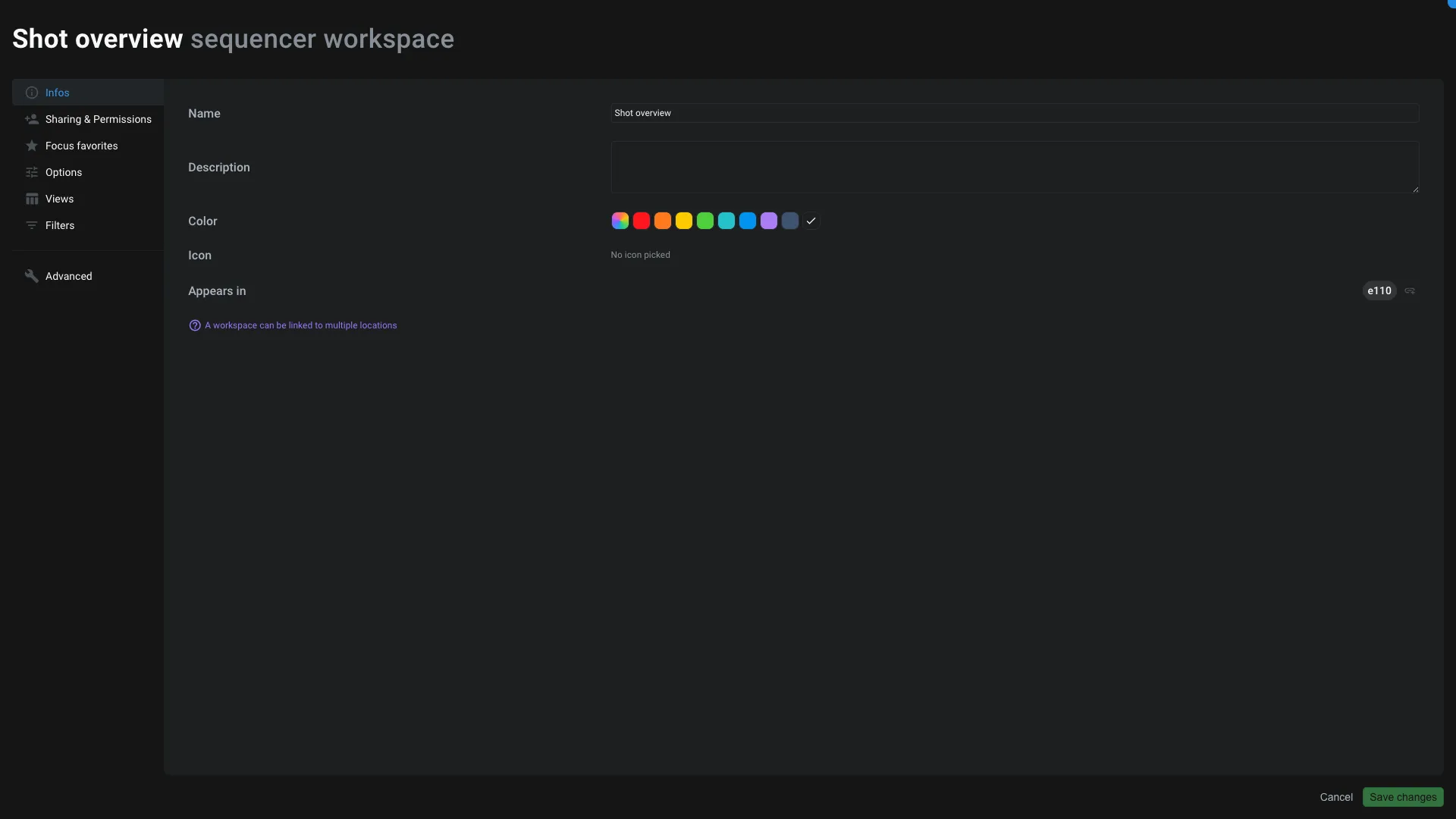
Infos
In the tab, you can see and edit the following information:
- The name of the workspace
- The description of the workspace
- The color of the workspace
- The icon of the workspace
- The location of the workspace. A workspace can be instantiated (clone) in multiple locations to avoid duplicating the same workspace.
Sharing & permissions
Like on any other items, you can define the permissions of the workspace. You can remove participant to hide the workspace from them. And you can also restrict their permissions to read-only, to avoid them being able to edit the workspace (like creating, moving or deleting columns, changing filters, ...).
Those permissions are only for the workspace itself (filters, column, ...). The content of a table, like the status of a task, is managed on the task itself.
Favorites
You can add a workspace as a favorite to access it quickly from the Focus interface and the Studio interface.
You can also add as favorite for other users, so they don't have to do it themselves.
Options
This is where you can edit some options of the workspace:
- Display: some workspaces are compatible with multiple display like
card,table, ... - Sort: you can define the default sort of the workspace
- Groups: you can define the default groups of the workspace. A group is a way to regroup items together, like based on their parent (ex: shots in a sequence), or based on their status, ...
More details about those options can be found in the dedicated section.
Views
A View is used in workspaces to regroup columns together.
From this interface you can define the height of the lines of your table and enable/disable the default view.
You can also create a new view or edit an existing one. To edit a view click on the icon. It will open the view editor.
You can create multiple view to regroup columns together. Since a view is an item, you can clone views into other workspaces.
Filters
All options related to filters are available here :
- Search: you can search for a specific keyword
- Depth: you can define the search depth. More details about this concept can be found in the dedicated section.
- Quick filters: you can edit the quick filters. Quick filters are filters easily accessible from the workspace interface.
- Default filter: you can enable/disable the default filter. Most of the time this filter is used to hide hidden elements. You can disable this filter to unhide items.
- Saved filters: are predefined filters that you can enable/disable in one click.
Advanced
From here you can access the advanced options of the workspace:
- Quickeditor: open the workspace in the quickeditor
- Editor: open the workspace in the JSON editor
- Export: export the workspace in a JSON file. It's useful if you need to share a workspace with Aquarium support. Please note the export doesn't include the content of the table, only the workspace configuration.
- Creatable items: you can restrict the type of items available in the
Createbutton. - Edge type: by default Aquarium display items using
Childedge. In very specific cases you might want to display items using another edge type. This option is here for this purpose. - Direction: Aquarium is a nodal solution using a graph to structure your data. The graph that we use have a direction. By default, when you browse folders, you go from the parent to the children: you are going down. But in some cases you might want to go up. This option is here for this purpose. You can also use the
bothdirection to go up and down at the same time.
Sets
This tab is here to edit the sets of the workspace.
A SET is used in meshQL to store a query result and reuse it in other queries. Most of the time it's a feature used by technical users to optimize workspace loading time.
A set can be used in a column, filter, group, ...
You can define multiple sets in a workspace. Each set has a name and a query. The query is a meshQL query that will be executed when the workspace is loaded. The name is important since it's how you can reference the set in other queries.
Performance
This tab give you insights about the performance of the workspace. A workspace have a score calculated based on it's filter and columns. A high score means that the workspace is fast and optimized. A low score means that the workspace is slow and my require some optimisations.
You can expand the last section Detailled active views analysis, to see more details about each views and there columns. For each view you can see it's performance impact on the global performance score. Meaning that you might to focus on the most impacting views to improve the performance of the workspace.
The depth can also have an impact on the performances, but it depends on the hierarchy and the structure of your data.
You can always reach our support team if you need help to improve the performance of your workspace. We are here to help you and we can provide you with some tips and tricks to improve the performance of your workspace.
